I have a question, I have traveled a lot and in all the countries I have been to, oral sex was always with a condom. Here in Montreal I have been surprised that the escorts always do oral sex without a condom and many even allow you to finish in the mouth. Isn't it very dangerous to do that? I understand that it is risky behavior and in some places it is prohibited. Have you had any bad experiences in this regard?
Oral sex without condom
- Thread starter elias77
- Start date
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
I have a question, I have traveled a lot and in all the countries I have been to, oral sex was always with a condom. Here in Montreal I have been surprised that the escorts always do oral sex without a condom and many even allow you to finish in the mouth. Isn't it very dangerous to do that? I understand that it is risky behavior and in some places it is prohibited. Have you had any bad experiences in this regard?
It is important to note that many service providers, particularly those offering the Girlfriend Experience (GFE), engage in unprotected oral activities. The rationale behind this is the fierce competition within the industry, as clients often prefer this type of service. Consequently, engaging in oral activities without a condom has become a prevalent phenomenon in Montreal. Although I am not a medical professional, I can confidently inform you that I have personally never contracted any infections from engaging in over many unprotected oral activities with numerous service providers. While the chance of contracting a sexually transmitted disease is rare by oral without a condom, but indeed very possible.
This has been discussed over and over again.
True risk cannot be calculated and varies in function of sti prevalence in population.
Some do it often and do not catch anything over several years.
But other have caught gono, chlam and even Syphillis. Certainly herpes and hpv as well.
Lets say the risk is reasonably low but if you worry, just ask for a CBJ…
True risk cannot be calculated and varies in function of sti prevalence in population.
Some do it often and do not catch anything over several years.
But other have caught gono, chlam and even Syphillis. Certainly herpes and hpv as well.
Lets say the risk is reasonably low but if you worry, just ask for a CBJ…
It is no secret that this particular topic has been extensively discussed within our community. However, considering the individual is a fresh addition to our platform, it is crucial that we grant them the respect they are entitled to as a new member, just as we should with any newcomer. Many often find themselves feeling anxious and unsure about initiating conversations on such matters. Therefore, it is essential that we create an environment that alleviates their insecurities and ensures their comfort.This has been discussed over and over again.
i've seen numerous escorts and always had BBBJ. Never caught anything. the important thing is to get tested regularly. I do get tested and hope everyone else is doing their part. I don't want to pass anything on and would love to have a safe play environment.
Yeah but rationnaly , getting tested do not reduce the risk here . It should be the girl testing herself often at least .i've seen numerous escorts and always had BBBJ. Never caught anything. the important thing is to get tested regularly. I do get tested and hope everyone else is doing their part. I don't want to pass anything on and would love to have a safe play environment.
But truth is there is a risk in getting oral sex from someone who give oral sex to stranger without a condom .
In term of Oral BBBJ remember that medically that saliva kills more germs than what one can find in a pussy.... more chances exponentially of barebacking than getting a BBBJ from a person with healthy saliva. In actual fact ur junk comes out cleaner than when it went in 
The risk of contracting a sexually transmitted infection from unprotected oral sex is generally lower compared to other forms of sexual activity, such as vaginal or anal sex. However, it is still possible to transmit or receive certain STIs through oral sex, though the likelihood varies depending on several factors:
1. Presence of an STI: The risk increases if either partner already has an active STI, such as herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis, or chlamydia. These infections can be transmitted through oral-genital contact.
2. Open sores or cuts: If there are any open wounds, sores, or cuts in the mouth or genital area, the likelihood of transmission may increase.
3. Ejaculation: If the partner ejaculates in the mouth, there is a higher risk of transmission for certain STIs, including gonorrhea or chlamydia.
4. Pre-existing conditions: People with weakened immune systems, such as those living with HIV, may have an increased risk of contracting or transmitting STIs.
It's essential to remember that condoms can help reduce the risk of STIs during oral sex.
1. Presence of an STI: The risk increases if either partner already has an active STI, such as herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis, or chlamydia. These infections can be transmitted through oral-genital contact.
2. Open sores or cuts: If there are any open wounds, sores, or cuts in the mouth or genital area, the likelihood of transmission may increase.
3. Ejaculation: If the partner ejaculates in the mouth, there is a higher risk of transmission for certain STIs, including gonorrhea or chlamydia.
4. Pre-existing conditions: People with weakened immune systems, such as those living with HIV, may have an increased risk of contracting or transmitting STIs.
It's essential to remember that condoms can help reduce the risk of STIs during oral sex.
i have received countless bbbjs over the years and never caught anything. According to the science, statistically, i should of caught something more than once, but I have not.
The risk for a male receiver of oral sex must be incredibly low. I beleive the risk is higher for the giver of bbbj, but still nothing life and death (AIDS cannot be transmitted that way)
I don't think this has anything to do with my situation (but maybe it does ) but I have ALWAYS showered after sex and often used mouthwash after performing daty.
) but I have ALWAYS showered after sex and often used mouthwash after performing daty.
The risk for a male receiver of oral sex must be incredibly low. I beleive the risk is higher for the giver of bbbj, but still nothing life and death (AIDS cannot be transmitted that way)
I don't think this has anything to do with my situation (but maybe it does
i always forget about that aspect...im not intact, maybe that has a role in my good luckIntact men have higher risk due to the skin being more mucusa like.
Respect man! I highly appreciate and respect people with your attitude.It is no secret that this particular topic has been extensively discussed within our community. However, considering the individual is a fresh addition to our platform, it is crucial that we grant them the respect they are entitled to as a new member, just as we should with any newcomer. Many often find themselves feeling anxious and unsure about initiating conversations on such matters. Therefore, it is essential that we create an environment that alleviates their insecurities and ensures their comfort.
I'm grateful for your kind words, my friend. Recognizing that every individual be treated with equal respect, regardless of their status as a new or old member, is crucial. It's also important to acknowledge that I would expect the same level of respect from a member if I were new and unfamiliar with this platform. By ensuring the new member feels comfortable, any potential anxiety they may have can be alleviated.Respect man! I highly appreciate and respect people with your attitude.
It's like crossing the street, even your light is green, there still a chance a drunk dude will hit you...
So? What you do? Never cross the street ?
I still do it, but just be careful, that's all.
Minimize the risk.
So? What you do? Never cross the street ?
I still do it, but just be careful, that's all.
Minimize the risk.
I think I'm going to post this in a new thread and ask the mods to pin it because I've reposted it so many times lol
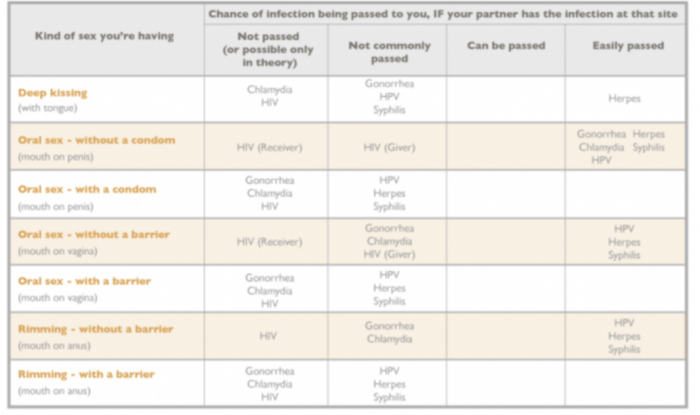
It's becoming less and less available as girls are realizing it isn't a mandatory service she has to provide. It's sites like this one where girls were under the impression she had to, to be relevant. But the longer I do this job, meet clients who mention other girls don't generally do it now, and talking with other girls, even those who offer pse, and require cbj even for that. The pressure to put ourselves at risk is lessoning. Especially learning it seems to be a local pressure and not something available everywhere.I have a question, I have traveled a lot and in all the countries I have been to, oral sex was always with a condom. Here in Montreal I have been surprised that the escorts always do oral sex without a condom and many even allow you to finish in the mouth. Isn't it very dangerous to do that? I understand that it is risky behavior and in some places it is prohibited. Have you had any bad experiences in this regard?
Besides personally the bj given is better when not on guard for the mans pre-ejaculate, or ejaculate happening in the mouth. Enough guys like to try and be stelthy and have it happen even if she refuses CIM. So the few ruin it for the many.
It is important to note that many service providers, particularly those offering the Girlfriend Experience (GFE), engage in unprotected oral activities. The rationale behind this is the fierce competition within the industry, as clients often prefer this type of service. Consequently, engaging in oral activities without a condom has become a prevalent phenomenon in Montreal. Although I am not a medical professional, I can confidently inform you that I have personally never contracted any infections from engaging in over many unprotected oral activities with numerous service providers. While the chance of contracting a sexually transmitted disease is rare by oral without a condom, but indeed very possible.
I've had BBBJ my whole life with all my girlfriends and never had problem.
Clean and clear with SPs so far...
The risk are very low but possible...
Everybody has their own limits when it comes to risk tolerance and management. I never caught anything my entire life, call me lucky if you want.I've had BBBJ my whole life with all my girlfriends and never had problem.
Clean and clear with SPs so far...
The risk are very low but possible...
You can easily get an STD from a BBBJ. Though, I’ve been lucky and haven’t caught anything yet. I don’t know if it’s my imagination but I think the risk of getting it from a SP is less likely than someone you would meet in a bar because they have a higher education level on STDs.
Also, I find I tend to get annoyed if it isn’t offered. Maybe, I’ve been spoiled from my experiences with SPs.
Also, I find I tend to get annoyed if it isn’t offered. Maybe, I’ve been spoiled from my experiences with SPs.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 54
- Views
- 7K
- Replies
- 26
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 86
- Views
- 3K






